Page 33 - SREENARAYANAGURU OPEN UNIVERSITY
P. 33
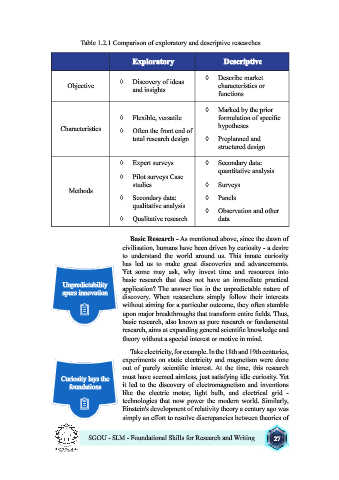
Table 1.2.1 Comparison of exploratory and descriptive researches
Exploratory Descriptive
◊ Describe market
◊ Discovery of ideas
Objective characteristics or
and insights
functions
◊ Marked by the prior
◊ Flexible, versatile formulation of specific
Characteristics ◊ Often the front end of hypotheses
total research design ◊ Preplanned and
structured design
◊ Expert surveys ◊ Secondary data:
quantitative analysis
◊ Pilot surveys Case
studies ◊ Surveys
Methods
◊ Secondary data: ◊ Panels
qualitative analysis
◊ Observation and other
◊ Qualitative research data
Basic Research - As mentioned above, since the dawn of
civilisation, humans have been driven by curiosity - a desire
to understand the world around us. This innate curiosity
has led us to make great discoveries and advancements.
Yet some may ask, why invest time and resources into
basic research that does not have an immediate practical
Unpredictability application? The answer lies in the unpredictable nature of
spurs innovation
discovery. When researchers simply follow their interests
without aiming for a particular outcome, they often stumble
upon major breakthroughs that transform entire fields. Thus,
basic research, also known as pure research or fundamental
research, aims at expanding general scientific knowledge and
theory without a special interest or motive in mind.
Take electricity, for example. In the 18th and 19th centuries,
experiments on static electricity and magnetism were done
out of purely scientific interest. At the time, this research
Curiosity lays the must have seemed aimless, just satisfying idle curiosity. Yet
foundations it led to the discovery of electromagnetism and inventions
like the electric motor, light bulb, and electrical grid -
technologies that now power the modern world. Similarly,
Einstein's development of relativity theory a century ago was
simply an effort to resolve discrepancies between theories of
SGOU - SLM - Foundational Skills for Research and Writing 27